this post was submitted on 14 Apr 2024
328 points (94.1% liked)
linuxmemes
21172 readers
962 users here now
Hint: :q!
Sister communities:
- LemmyMemes: Memes
- LemmyShitpost: Anything and everything goes.
- RISA: Star Trek memes and shitposts
Community rules (click to expand)
1. Follow the site-wide rules
- Instance-wide TOS: https://legal.lemmy.world/tos/
- Lemmy code of conduct: https://join-lemmy.org/docs/code_of_conduct.html
2. Be civil
- Understand the difference between a joke and an insult.
- Do not harrass or attack members of the community for any reason.
- Leave remarks of "peasantry" to the PCMR community. If you dislike an OS/service/application, attack the thing you dislike, not the individuals who use it. Some people may not have a choice.
- Bigotry will not be tolerated.
- These rules are somewhat loosened when the subject is a public figure. Still, do not attack their person or incite harrassment.
3. Post Linux-related content
- Including Unix and BSD.
- Non-Linux content is acceptable as long as it makes a reference to Linux. For example, the poorly made mockery of
sudoin Windows. - No porn. Even if you watch it on a Linux machine.
4. No recent reposts
- Everybody uses Arch btw, can't quit Vim, and wants to interject for a moment. You can stop now.
Please report posts and comments that break these rules!
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
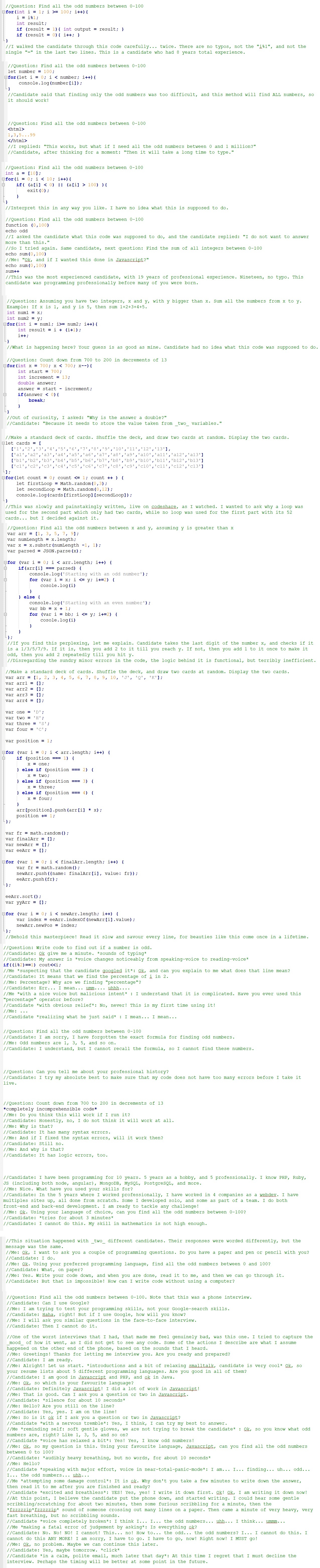
I always feel bad when I try out a new coding problem for interviews because I feel I'm going to offend candidates with such an easy problem (I interview mostly for senior positions). And I'm always shocked by how few are able to solve them. The current problem I use requires splitting a text into words as a first step. I show them the text, it's the entire text of a book, not just some simple sentence. I don't think I've had a single candidate do that correctly yet (most just split by a single space character even though they've seen it's a whole book with newlines, punctuation, quotes, parentheses, etc).
That is totally a non-trivial problem, which requires a lot more conception before it can be solved. Even for English, this is not well defined: Does "don't" consist of one or two words? Should "www.google.com" be split into three parts? Etc.
And don't let me start with other languages: In French, "qu'est-ce que" is one word (what). In the German sentence "Ruf mich an.", the "Ruf an" is one word (call) while mich is another word (me). In Chinese, you usually don't even have spaces between words.
If I got that feature request in a ticket, I'd send it back to conception. If you asked me this question in an interview, I'd ask if you wanted a programmer, a requirements analysis, or a linguist and why you invite people for a job interview if you don't even know what role you are hiring for.
They're both parts of the verb anrufen but I've never heard someone say they're still a single word when there's a space (or more) inbetween
There is no single definition, for what a word is, which is exactly my point. Some linguists even argue that "word" is inherently undefinable and refuse to use it as a category.
One common (but still ambiguous) definition is though, that a word is the smallest unit in a language that can stand on its own and conveys a meaning. By that definition, "Ruf .. an" is one word, as "an" is not a word by itself. It might not be too obvious, as "an" can also be a word by itself , just not in this context. Another example, where it's more obvious, is "innehalten". "Inne" is not a word, it has no meaning by itself, it cannot be used on its own, so in the sentence "halte kurz inne", "halte inne" is one word. Another example would be "Stelle etwas dar", where "dar" is obviously not a word by itself.
Fun fact: Verb literally means word in Latin, so saying they are the part of the same verb, but not the same word is kind of an oximoron.