this post was submitted on 18 Sep 2024
1220 points (97.4% liked)
Microblog Memes
5787 readers
2224 users here now
A place to share screenshots of Microblog posts, whether from Mastodon, tumblr, ~~Twitter~~ X, KBin, Threads or elsewhere.
Created as an evolution of White People Twitter and other tweet-capture subreddits.
Rules:
- Please put at least one word relevant to the post in the post title.
- Be nice.
- No advertising, brand promotion or guerilla marketing.
- Posters are encouraged to link to the toot or tweet etc in the description of posts.
Related communities:
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
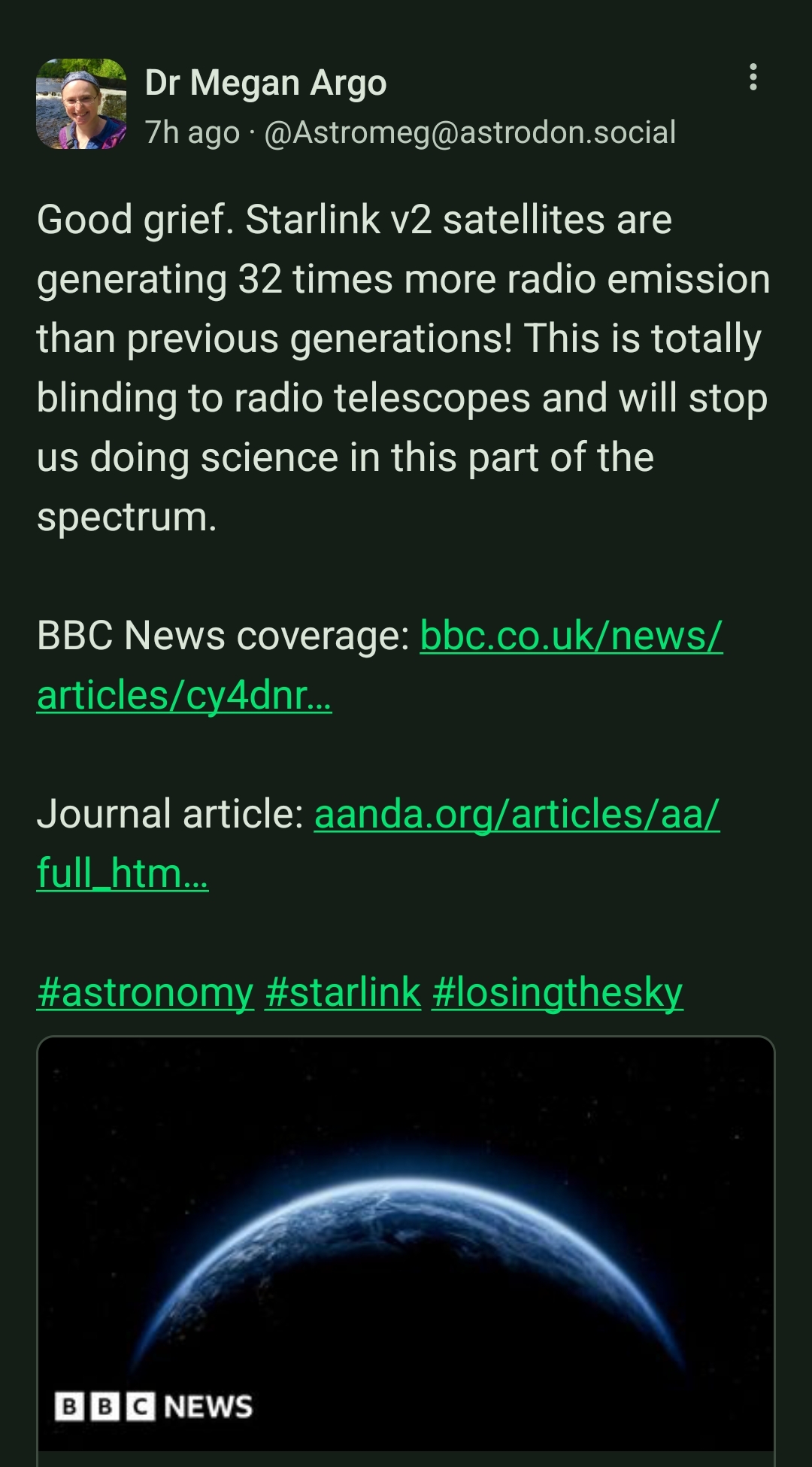
We could and should be doing both ground and orbital radio telescope observations. One really interesting idea I've seen floated is to put one on the far-side of the moon; it'd be shielded from all our radio emissions but, of course, it would be somewhat suspectable to interference from the sun for weeks at a time.
What I've never understood about Starlink is how it's better than existing satellite internet beamed from geosynchronous craft... like, geosync is crowded (especially over North America and Europe), but it's not so crowded we couldn't put a couple more transponders up there. Objects in geosync rarely have the astronomical side effects that Starlink is apparently causing. It would even solve the Starlink issue of having to have an expense af receiver with active tracking... just nail up a stationary ku-band dish that doesn't need to move ever. This is already solved technology.
The problem with geosynchronous orbit is that you need to be at a high altitude to maintain it. That increases the packet round trip time to a receiver on the ground. Starlink satellites orbit low enough to give a theoretical 20ms ping. A geostationary satellite would be at best 500ms. It’s fine for some tasks but lousy for applications that need low latency, like video calling.
Is there any way to improve that? Or is it a hard limit due to physics?
Unfortunately it’s a hard limit due to the speed of light. Theoretically you could use quantum entanglement to get around it, but then of course you wouldn’t need the satellites anymore.
no, you couldn't. You can't use quantum entanglement to send information. Only random noise.
Sorry, I meant theoretically as in “at some distant point in the future where we’ve figured out how to make it work.” I probably read too much science fiction.
it physically cannot work. ever. That's just how entanglement works. We know that much.
That's not true either unfortunately
Science fiction quantum entanglement is not the same as real life quantum entanglement. Science fiction has spooky action at a distance, real life doesn't.
The speed of light is the speed of causality, the speed of information. It is physically impossible to send information at speeds greater than the speed of light.
In real life, all quantum entanglement means is that you can entangle two particles, move them away from each other, and still know that when you measure one, the other will have the opposite value. It's akin to putting a red ball in one box and a blue ball in another, then muddling them up and posting them to two addresses. When opening one box, you instantly know that because you saw a red ball, the other recipient has a blue one or vice versa, but that's it. The extra quantum bit is just that the particles still do quantum things as if they're a maybe-red-maybe-blue superposition until they're measured. That's like having a sniffer dog at the post office that flags half of all things with red paint and a quarter of all things with blue paint as needing to be diverted to the police magically redirect three eighths of each colour instead of different amounts of the two colours. The balls didn't decide which was red and which was blue until the boxes were opened, but the choice always matches.